
All four of Greece’s systemic banks announced successful 2021 SSM stress test results on Friday, completed via the European Central Bank (ECB), and under common methodological rules defined by the European Banking Authority (EBA) and using macroeconomic and market scenario assumptions published in late January 2021.
In its press release, National Bank of Greece noted that “…National Bank of Greece S.A. announces the successful completion of the 2021 SSM Stress Test, led by the European Central Bank (ECB), under the common methodological rules defined by the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the macroeconomic and market scenario assumptions published on 29/01/2021.
The Stress Test Exercise was based on a Static balance sheet approach, thus factoring in the Group financial and capital position of 31.12.2020 as a starting point, conducting a 3-year horizon stress simulation (2021-23), under a Baseline and an Adverse scenario.
Starting from a 31.12.2020 Fully Loaded (FL) CET 1 ratio of 12.8% (15.7% on Transitional basis), the Baseline scenario resulted in a capital accretion of 270bps over the 3-year horizon, with the FL CET 1 ratio reaching the level of 15.5% in 2023. Under the Adverse scenario, the FL CET 1 ratio maximum depletion reached 6.4% in year 2022, while the respective FL CET 1 ratio for 2023 settled at 6.4%.
Given the Static balance sheet methodology, the 2021 SSM Stress Test does not incorporate capital accretive results post 31.12.2020.
National Bank of Greece S.A. Group’s FL CET1 ratio at 31 March 2021 stood at 14.0% (pro-forma for the profits of the period), 120bps higher relative to the starting point of the Stress Test, while the combined impact on Total Capital Ratio post completion of the Frontier and Ethniki Insurance transactions of c170bps is also not factored in. According to the Bank’s pro-forma calculations, taking into account these developments, the Total Capital ratio increases by nearly 300bps.
Alpha Bank followed with its press release: “…Alpha Services and Holdings successfully concluded the 2021 EU-wide Stress Test. ▪ The Stress Test was conducted based on a static balance sheet approach under a baseline and an adverse macro scenario with a 3-year forecasting horizon (2020-2023). No hurdle rate or capital thresholds were applied for this exercise but was designed to be used as an important input in the Supervisory Evaluation Process (SREP). ▪ The starting point of the exercise was December 31st, 2020, when the Bank had a CET1 transitional ratio of 17.1%, a CET1 fully loaded ratio of 14.6% as well as a Leverage ratio (transitional) of 12.5% and a Leverage ratio (fully loaded) of 10.7%. ▪ Under the baseline scenario, the capital generation for the 3-year period was 2.8% absorbing 2.4% IFRS 9 phase-in, resulting in 2023, CET1 transitional ratio of 17.4%. The 2023 CET1 fully loaded ratio reached 17.3% while the 2023 Leverage ratio (fully loaded) came to 13.0%. ▪ Under the adverse scenario, the 2023 CET1 transitional ratio stood at 8.4%, largely driven by the negative impact of Credit Risk. The 2023 CET1 fully loaded ratio came to 8.3% while the 2023 Leverage ratio (fully loaded) resulted in 6.1%. The capital depletion for the 3-year period in the adverse scenario was 8.7%, of which 2.4% is due to IFRS 9 impact and 6.3% as a result of the Stress Test parameters. In 2022, the Bank registered its lowest point in CET1 fully loaded with 8.1%. ▪ The Stress Test methodology does not take into account capital strengthening (i.e. Tier II issuance, Share Capital Increase) and balance sheet de-risking (i.e. Galaxy transaction), events post December 31st, 2020. Pro-forma1 with the Share Capital Increase for the baseline scenario, the 2023 CET1 fully loaded ratio reached 19.1%, while the 2023 Leverage ratio (fully loaded) came to 14.4%. Under the adverse scenario, the 2023 CET1 fully loaded ratio stood at 10.2%, while the 2023 Leverage ratio (fully loaded) came to 7.6%.”
On its part, Eurobank announced: “Eurobank Ergasias Services and Holdings S.A. (Eurobank Holdings) announces that it successfully completed the 2021 SSM Stress Test (ST) which was coordinated and conducted by the European Central Bank (ECB).
The following figures summarize the performance of Eurobank Holdings Group at consolidated basis under the Baseline and Adverse scenarios of the ST exercise. The starting point of the ST exercise is the financial and capital position of the Group as at 31/12/20201. The ST horizon covers the period until the end of 2023.
Under the Baseline scenario, the Group is capital accretive by 290bps over the 3-year ST horizon, reaching, on a Fully Loaded (FL) basis, total Capital Adequacy (CAD) ratio of 17.5%, and Core Tier 1 (CET 1) ratio of 14.9% as at the end of 2023.
Under the Adverse scenario, the capital depletion in terms of FL CET 1 ratio amounts to 433bps as at the end of 2023 and to 517bps at the year with the highest impact (2021). Accordingly, the FL CET 1 ratio stands at 7.6% as at the end of 2023 and at 6.8% at the year with the highest impact (2021). On a transitional basis, the CET 1 ratio at the end of 2023 stands at 8%.”
Eurobank CEO Fokion Karavias said:
“We are particularly pleased with the performance of our Group in the ECB stress test. Especially under the severe assumptions of the adverse scenario, the key indicator of capital depletion confirmed the bank’s resilience and ability to withstand a significant downturn. As the first Greek bank to complete the cleanup of legacy NPEs, we are focusing our efforts in financing households and businesses, and in promoting growth in all our markets”.
Finally, Piraeus Bank stated that ‘…Piraeus Financial Holdings SA (“Piraeus”) announces that it has successfully completed the 2021 SSM Stress Test Exercise (“exercise”) conducted by the European Central Bank.
The reference balance sheet for the exercise is that of 31 December 2020, the time horizon extends to the end of 2023 and the exercise assesses a baseline and an adverse scenario.
Under the baseline scenario, the fully loaded total capital ratio stands at 17.1%, while the CET1 ratio at 15.0% at year-end 2023. The baseline scenario was capital accretive by c.365bps versus 2020.
The adverse scenario results to a depletion of c.480bps for the 3-year period. The respective depletion in the 2018 Stress Test Exercise was c.770bps. The resulting fully-loaded capital ratios for year-end 2023 are 8.6% for total capital and 6.5% for CET1. The adverse scenario results to c.610bps depletion at the year with the highest impact (2021).
The exercise was based on a static balance sheet approach and does not incorporate initiatives post 31 December 2020. In the context of its “Sunrise” plan, Piraeus has completed a €1.38bn share capital increase and a €0.6bn AT1 issuance in Q2.2021. Taking into account these actions, the fully loaded ratios under the adverse scenario for 2023 are adjusted to c.13.5% total capital and c.10.0% CET1 as per proforma Piraeus calculations.”
Latest News

Cost of Living: Why Greece’s 3% Inflation Is Raising Alarm
Greece appears to be in a more difficult position when it comes to price hikes, just as we enter the era of Trump’s tariffs.

Fitch Ratings Upgrades the Four Greek Systemic Banks
NBG’s upgrade reflects the bank’s ongoing improvements in its credit profile, Fitch notes in its report, including strong profitability, a reduction in non-performing exposures (NPEs), and lower credit losses

Trump to Announce Sweeping New Tariffs Wednesday, Global Retaliation Expected
With Trump's announcement just hours away, markets, businesses, and foreign governments are bracing for the fallout of one of the most aggressive shifts in U.S. trade policy in decades.

Inflation in Greece at 3.1% in March, Eurostat Reports
Average inflation in the eurozone settled at 2.2%, compared to 2.3% in February

Greece’s Unemployment Rate Drops to 8.6% in February
Despite the overall decline, unemployment remains higher among women and young people.

Jerry Kalogiratos Highlights Key Role of Energy Transition and Data Demand in LNG Outlook
Energy transition and the prospects of LNG were discussed at Capital Link’s 19th Annual International Maritime Forum, during a panel discussion with Jerry Kalogiratos (Capital Clean Energy Carriers Corp.)

Santorini Safe and Ready for a Dynamic Tourism Season
Authenticity, cultural heritage, and genuine experiences at the center of Santorini's new promotional campaign

Electricity Bills: Greece Announces Reduced Tariffs Schedule
Greece will now offer lower electricity rates between 11:00-15:00 and 02:00-04:00
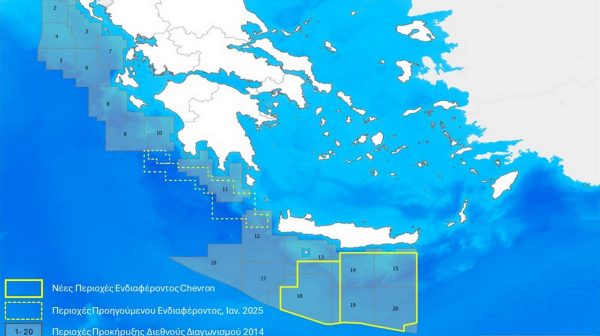
Chevron Confirms Eyeing Natural Gas Exploration South of Crete
Chevron recently declared its intent to explore a third area, south of the Peloponnese.
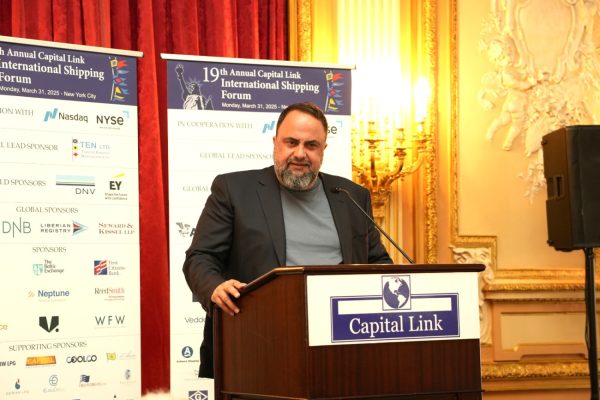

Evangelos Marinakis: A time of change from which shipping can benefit
Speaking at the 19th Annual Capital Link International Shipping Forum Evangelos Marinakis stressed the challenges that shipping faces today












![Τουρκία: Μεγάλες βλέψεις για παραγωγή ηλεκτρικών οχημάτων [γράφημα]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/ot_turkish_autos-90x90.png)











![ΕΛΣΤΑΤ: Αυξήθηκε η οικοδομική δραστηριότητα κατά 15,6% το Δεκέμβριο [πίνακες]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/DSC9655-2-1024x569-1-90x90.jpg)

















 Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης
Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης