
The great debt reduction achieved by Greece is highlighted by Unicredit in its analysis. As the investment house’s analysts explain, this reduction in debt was a result of both higher GDP and inflation and a smaller primary surplus.
According to Unicredit’s report, the pandemic has led to a sharp increase in the euro area’s public debt as a percentage of GDP, partly due to strong fiscal measures to support incomes and partly due to the decline in GDP. The public debt-to-GDP ratio rose by 13 percentage points for the Eurozone in 2020, ranging from an increase of 9 percentage points in Germany (reflecting the comparatively small decline in German GDP) to a 26 percentage point increase in Greece, which had the worst performance.
Other countries
However, according to the latest estimates of the European Commission, Greece has recorded a cumulative decrease of 35 percentage points in its public debt/GDP ratio, a percentage significantly greater than the increase caused by the crisis. Portugal has also fully reversed the impact of the pandemic crisis on its public debt, while Italy has almost halved it.
For Spain a reduction of around 6 percentage points is estimated over two years and less for France. Germany has seen only a marginal decline in its public debt-to-GDP ratio over the past two years, having seen a comparatively small increase during the pandemic crisis.
Greater contribution
The declines in public debt/GDP ratios over the past two years are mainly due to rapid growth in nominal GDP. Greece, in particular, had a much larger contribution from nominal GDP growth than the other countries due to significant growth in real GDP and the GDP deflator in both years. In addition, a narrower primary deficit (on an annual basis) contributed to the downward adjustment.
UniCredit estimates that debt-to-GDP ratios in Eurozone countries will likely decline slightly or stabilize in the coming years.
The avalanche phenomenon
Beyond that, UniCredit Bank explains that the “avalanche effect”, i.e. the effect on the public debt-to-GDP ratio of the difference between the average interest rate paid on public debt and the nominal GDP growth rate. If the average interest rate paid on government debt is lower (higher) than the nominal growth rate of GDP, then the debt-to-GDP ratio tends to decrease (increase).
The European Commission estimates that Italy will show a primary deficit of around 1% of GDP for 2022, while for France, this figure is forecast to rise to just over 3% of GDP. In contrast, Portugal is projected to achieve a balanced primary budget in 2022, and this is expected to support the downward adjustment of its public debt-to-GDP ratio.
Latest News

New Exposé by Domumento Reveals Nefarious Triangular Link of ‘Black Money’ with New Democracy, Blue Skies, & Truth Team
The latest exposé by the Documentonews.gr news site lays bare what appears to be a surreptitious path of indirect financing of ND through the business sector—transactions that, as widely understood, rarely occur without expectations of reciprocal benefit
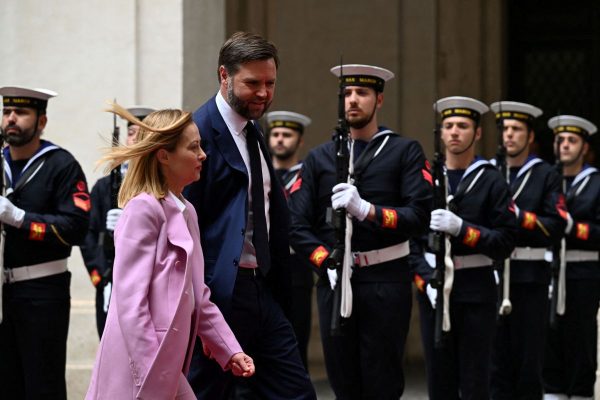

PM Meloni Meets Vice President Vance in Rome Signalling Optimism on Ukraine Talks
Meloni emphasized the strength and strategic value of the Italy-U.S. partnership.

Airbnb: Greece’s Short-Term Rentals Dip in March Amid Easter Shift
Data from analytics firm AirDNA shows that average occupancy for short-term rentals dropped to 45% in March, down from 49% the same month last year.

Easter Week in Greece: Holy Friday in Orthodoxy Today
At the Vespers service on Friday evening the image of Christ is removed from the Cross and wrapped in a white cloth
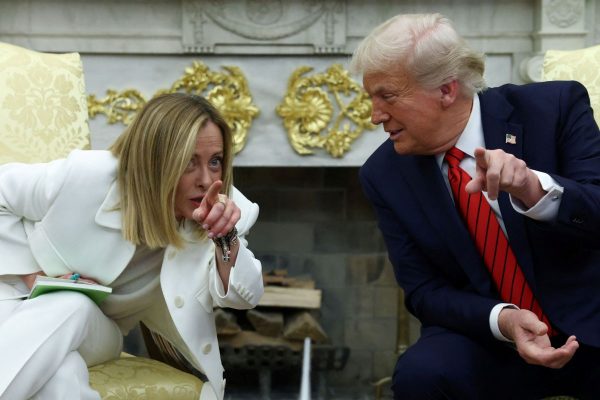

Meloni and Trump Meet in Washington, Vow to Strengthen Western Ties
“I am 100% sure there will be no problems reaching a deal on tariffs with the EU—none whatsoever,” Trump stressed.

ECB Cuts Interest Rates by 25 Basis Points in Expected Move
The ECB’s Governing Council opted to lower the deposit facility rate—the benchmark for signaling monetary policy direction—citing an updated assessment of inflation prospects, the dynamics of underlying inflation, and the strength of monetary policy transmission.

Current Account Deficit Fell by €573.2ml Feb. 2025: BoG
The improvement of Greece’s current account was mainly attributed to a more robust balance of goods and, to a lesser extent, an improved primary income account

Hellenic Food Authority Issues Food Safety Tips for Easter
Food safety tips on how to make sure your lamb has been properly inspected and your eggs stay fresh.

Greek Kiwifruit Exports Smash 200,000-Ton Mark, Setting New Record
According to data by the Association of Greek Fruit, Vegetable and Juice Exporters, Incofruit Hellas, between September 1, 2024, and April 17, 2025, kiwifruit exports increased by 14.2%.

Easter Tourism Boom: Greece Sees 18.3% Surge in Hotel Bookings
Among foreign markets, Israel has emerged as the biggest growth driver, with hotel bookings more than doubling—up 178.5% year-on-year.






![Πλημμύρες: Σημειώθηκαν σε επίπεδα ρεκόρ στην Ευρώπη το 2024 [γράφημα]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/FLOOD_HUNGRY-90x90.jpg)





![Airbnb: Πτωτικά κινήθηκε η ζήτηση τον Μάρτιο – Τι δείχνουν τα στοιχεία [γράφημα]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/airbnb-gba8e58468_1280-1-90x90.jpg)











![Επιχειρήσεις: Με τι επιτόκιο δανείζονται – Πώς θα ξεκλειδώσει περισσότερη ρευστότητα [γράφημα]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/daneia-trapezes-768x432-1-600x338.jpg)














 Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης
Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης