
It may, at first, look like that the monster of inflation is restrained, however with a second reading we are in the second wave of rising prices, which seems stronger and, above all, more drastic.
The market is expecting new price hikes in basic products from the beginning of 2023, which is causing strong concern among consumers.
Inflation in November narrowed to 8.5% from 9.1% in October and 12.1% in June, but prices remain higher and hikes are in full swing. Despite the reduction in inflation, prices are galloping as the problem spreads with increasing intensity throughout the economy with basic food prices registering an annual increase of 11.3% to as much as 25.3% (bread, cereals, meat, dairy, oils, coffee).
Not only are price hikes on the supermarket shelf unabated, but, based on the increased wholesale invoices that have reached the chains’ books from suppliers, any deflationary trends will take a long time to see through to consumers’ pockets.
And the reason is the stocks of products that were produced at a significantly higher cost. Thus, even if the de-escalation in energy inflation continues (at a ‘technical’ or non-technical level), the stock of more expensive consumer goods does not leave room for price cuts for quite some time.
Steady rise
Based on the economic climate surveys, the companies that stated that they increased their prices are constantly increasing as from 6.6% in the 2nd half of 2020, they reached 23.6% in the 1st half of 2021, to 34, 8% in the 2nd half of 2021 and to 59.2% in the 1st half of 2022.
Correspondingly, in the same period, we see a significant decrease in the number of companies that stated that they reduced their prices, as well as those that kept them constant.
The largest concentrations of companies that increased prices during the second half of 2021 were observed in commercial (43.8%) and manufacturing firms (50%).
On the other hand, companies operating in the service sector seem to have, in general, held back their prices, as 16.7% of them increased prices, compared to 10.9% that reduced prices and 72% that kept them stable.
In the first half of 2022, at a sectoral level, businesses in trade and manufacturing stated to a greater extent that they increased their prices (66.2% and 66.3% respectively) compared to businesses in the broader service sector (47 .9%).
BoG sounds the “alarm”
At the same time, the interim report of the Bank of Greece (BoG) shows continued price hikes for at least 2 more years.
As it follows, inflation will remain at a very high level in 2023 as well, while in 2024 it is expected to be almost twice the limit set by the European Central Bank. Thus, price levels in Greece acquire characteristics of permanence, at a time when households “see” their real income losing value.
Based on what the BoG forecasts, the harmonized index of consumer prices from 9.4% this year at average levels, will slow down to 5.8% in 2023 and further to 3.6% in 2024 mainly due to the estimated de-escalation of the prices of energy, but also the negative effect of the basis of comparison. In other words, during the next two years these factors are expected to continue to affect the Greek economy.
Latest News

Cost of Living: Why Greece’s 3% Inflation Is Raising Alarm
Greece appears to be in a more difficult position when it comes to price hikes, just as we enter the era of Trump’s tariffs.

Fitch Ratings Upgrades the Four Greek Systemic Banks
NBG’s upgrade reflects the bank’s ongoing improvements in its credit profile, Fitch notes in its report, including strong profitability, a reduction in non-performing exposures (NPEs), and lower credit losses

Trump to Announce Sweeping New Tariffs Wednesday, Global Retaliation Expected
With Trump's announcement just hours away, markets, businesses, and foreign governments are bracing for the fallout of one of the most aggressive shifts in U.S. trade policy in decades.

Inflation in Greece at 3.1% in March, Eurostat Reports
Average inflation in the eurozone settled at 2.2%, compared to 2.3% in February

Greece’s Unemployment Rate Drops to 8.6% in February
Despite the overall decline, unemployment remains higher among women and young people.

Jerry Kalogiratos Highlights Key Role of Energy Transition and Data Demand in LNG Outlook
Energy transition and the prospects of LNG were discussed at Capital Link’s 19th Annual International Maritime Forum, during a panel discussion with Jerry Kalogiratos (Capital Clean Energy Carriers Corp.)

Santorini Safe and Ready for a Dynamic Tourism Season
Authenticity, cultural heritage, and genuine experiences at the center of Santorini's new promotional campaign

Electricity Bills: Greece Announces Reduced Tariffs Schedule
Greece will now offer lower electricity rates between 11:00-15:00 and 02:00-04:00
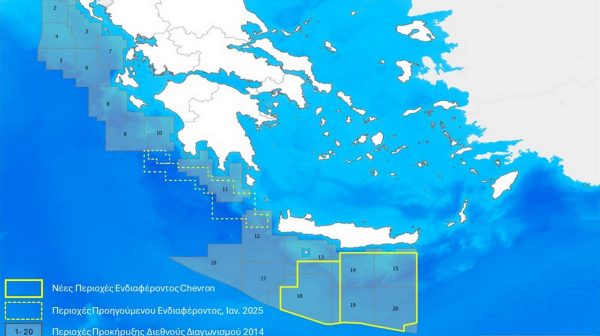
Chevron Confirms Eyeing Natural Gas Exploration South of Crete
Chevron recently declared its intent to explore a third area, south of the Peloponnese.
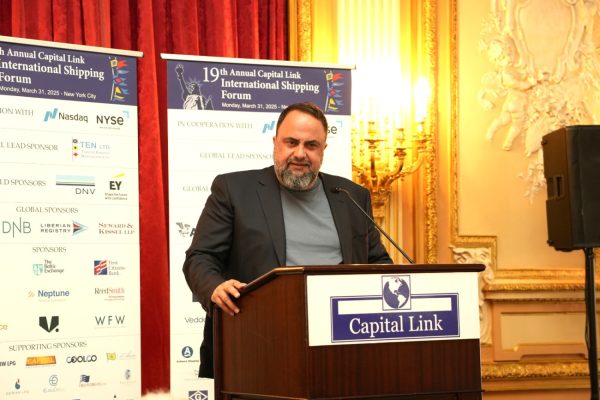

Evangelos Marinakis: A time of change from which shipping can benefit
Speaking at the 19th Annual Capital Link International Shipping Forum Evangelos Marinakis stressed the challenges that shipping faces today












![Τουρκία: Μεγάλες βλέψεις για παραγωγή ηλεκτρικών οχημάτων [γράφημα]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/ot_turkish_autos-90x90.png)











![ΕΛΣΤΑΤ: Αυξήθηκε η οικοδομική δραστηριότητα κατά 15,6% το Δεκέμβριο [πίνακες]](https://www.ot.gr/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/DSC9655-2-1024x569-1-90x90.jpg)















 Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης
Αριθμός Πιστοποίησης